Guide to Aluminum Extrusion: Process and Advantages
Contents
- 1. What Is Aluminum Extrusion?
- 2. Advantages of Aluminum Extrusion
- 3. Aluminum Extrusion Process
- 3.1 Aluminum Ingot Preparation
- 3.2 Heating
- 3.3 Extrusion
- 3.4 Cooling
- 3.5 Stretching and Straightening
- 3.6 Cutting and Surface Treatment
- 4. Applications of Aluminum Extrusion
- 4.1 Building and Construction
- 4.2 Automotive Industr
- 4.3 Aerospace Industry
- 4.4 Electronics Industry
- 4.5 Sports and Leisure Equipment
- 5. Environmental Strategies in the Aluminum Extrusion Industry
- 5.1 Recycling aluminum scrap during production
- 5.2 Selecting eco-friendly materials and improving environmental controls
- 6. The Future of Aluminum Extrusion
- 7. FAQ: Common Questions About Aluminum Extrusion Process
- 8. Conclusion
Aluminum is all around us — from the frames of our doors and windows to the vehicles we drive and even the aircraft flying overhead. But how do we transform this strong yet lightweight metal into such a wide variety of shapes?
Due to its flexibility and workability, aluminum can be shaped almost like clay to meet the needs of modern industries. Aluminum extrusion is a key part of this process where the material is shaped into a basic profile that can later be machined. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the basics of aluminum extrusion process, its advantages, applications, environmental trends, and the future of this essential manufacturing process.
What Is Aluminum Extrusion?
Aluminum extrusion is a manufacturing process where heated aluminum alloy is forced through a specially shaped die to create parts with a consistent cross-sectional profile. Imagine squeezing whipped cream through the star-shaped tip of a pastry bag. That’s very close to how aluminum extrusion works. When aluminum is heated, it becomes soft and flexible—just like whipped cream. At that point, it can be forced through a die (a metal mold) shaped into a specific profile. For example, a square die produces continuous square tubes ideal for frames, rails, or supports, while T- or U-shaped dies create matching cross-sections suitable for structural framing, sliding tracks, or architectural assemblies.
Advantages of Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion offers several key advantages that make it a go-to choice for modern manufacturing:
Lightweight with High Strength
Aluminum is significantly lighter than steel—about one-third the weight—while still offering impressive strength. This balance makes it ideal for products where reducing weight without compromising durability is critical. It’s widely used in car frames, aircraft components, and bicycle frames to lessen the burden for greater speed and efficiency.
Excellent Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum naturally forms a thin layer of oxide when exposed to air, creating a protective barrier that helps it resist rust and corrosion. This makes it especially useful for outdoor applications, such as window frames or railing, where it must endure moisture and changing weather conditions.
Recyclable and Sustainable
Aluminum is one of the most recyclable metals on the planet. It can be melted down and reused indefinitely without losing quality, and recycling it requires only about 5% of the energy needed to produce new aluminum. This makes it a sustainable material choice for manufacturers looking to lower their environmental impact.
Good Thermal Conductivity
Aluminum’s excellent ability to transfer heat makes it especially useful in electronics and temperature-sensitive equipment. It’s often used for cooling parts like LED light casings, where the aluminum housing acts both as a structural shell and as a heat-dissipating surface to prevent overheating and extend product lifespan.
Highly Customizable Designs
The extrusion process allows aluminum to be formed into a vast range of complex and precise cross-sectional shapes. From decorative trim and architectural moldings to intricate channels for lighting systems or sliding tracks, manufacturers can achieve detailed and highly functional designs while keeping production efficient.
Easy Secondary Processing
After extrusion, aluminum profiles can be easily cut, machined, drilled, welded, or finished to meet specific application needs. Whether it’s anodizing for color and corrosion resistance, powder coating for aesthetics, or machining for precise part integration, aluminum is easy to work with—reducing production time and cost.
Aluminum Extrusion Process
The aluminum extrusion process typically follows these steps:
1.Aluminum Ingot Preparation (H3)
Selected aluminum alloy ingots are cut to a suitable length—typically around 18 to 24 inches, or about the length of an adult’s arm—and loaded into the extrusion press. Choosing the right size ensures consistent pressure during extrusion and optimal material flow through the die.
2. Heating
The aluminum ingots are then heated to approximately 450°C to 500°C, becoming flexible while still remaining solid. This plastic-like condition allows the material to be shaped effectively during the extrusion process without losing its structural integrity.
3. Extrusion
Once heated, the aluminum is forced through a steel die using strong mechanical pressure.The die determines the final cross-sectional shape of the product—be it a hollow square tube, a round pipe, or a custom profile for architectural or industrial use. This is the most critical step in defining the form and function of the extruded material.
4. Cooling
As soon as the aluminum exits the die, it is quickly cooled using air or water to solidify its shape and improve its strength. Fans or sprays are used to cool the material evenly and prevent warping.
5. Stretching and Straightening
During cooling, the metal can develop internal stresses due to uneven shrinkage or how the material flowed through the die. Stretching the profile helps realign the structure and relieve these stresses. This step also corrects any slight bending or distortion to ensure the finished product is straight.
6. Cutting and Surface Treatment
The final step involves cutting the extrusion into specified lengths, which can range from a few centimeters to several meters depending on the application. After cutting, the profiles may undergo surface treatments such as anodizing, powder coating, or chemical finishing. These treatments enhance corrosion resistance, appearance, and durability for end-use in industries such as construction, transportation, and electronics.
Applications of Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion plays a much bigger role in our lives than we often realize. From the electronic parts in your smartphone to the body of an airplane overhead, aluminum helps power, protect, and connect the world around us. Its lightweight strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance make it an essential material across many industries.
Building and Construction
Next time you glance at a window frame, a louver, or a modern door design, there’s a good chance aluminum extrusion is behind it. Durable and highly customizable, extruded aluminum profiles are a favorite for creating architectural elements that need to be both strong and visually appealing.
Machines like the JIH-CNC H-Type CNC Machining Center are built to handle long aluminum profiles with precision—ensuring that frames and structures fit perfectly and look flawless.
Automotive Industry
Look around any parking lot or traffic scene: car doors, window frames, and even bumper structures often owe their lightweight strength to aluminum extrusion. Reducing the weight of vehicles helps boost fuel efficiency, making aluminum a key player in today's drive toward greener transportation.
Aerospace Industry
If you spot a plane cruising overhead, chances are aluminum extrusion plays a major role. Parts like tail fins, wing ribs, and the main body of the aircraft rely on aluminum’s lightness and strength to keep them airborne safely and efficiently.
Electronics Industry
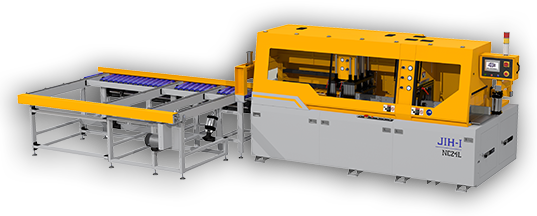
The device you’re reading this on—whether a smartphone, tablet, or laptop—likely depends on extruded aluminum parts. Heat sinks (which help cool down chips and batteries) and housings (the protective outer shells of devices) are often made with aluminum for its excellent thermal conductivity and strength. For precision cutting of these components, JIH-I’s NC24L high-production CNC sawing machine offers outstanding accuracy and efficiency, making it ideal for electronics manufacturing.
Sports and Leisure Equipment
From bicycles parked outside a café to scooters zipping down city streets, extruded aluminum helps make sports and leisure gear lightweight, sturdy, and built for everyday adventure.
Environmental Strategies in the Aluminum Extrusion Industry
As global awareness of environmental protection grows, the aluminum extrusion industry is adopting greener practices to reduce its environmental footprint. Key strategies include:
Recycling aluminum scrap during production
About 40% of aluminum cast into billets is scrapped before becoming a finished product—mainly from removing structural or surface defects.¹ By collecting, remelting, and reusing this leftover material directly within the production process, manufacturers can significantly reduce resource waste, lower production costs, and cut greenhouse gas emissions.
Selecting eco-friendly materials and improving environmental controls
Many companies are switching to environmentally friendly lubricants and cleaning agents to reduce harmful emissions. At the same time, they are enhancing wastewater and exhaust treatment systems to meet stricter environmental standards and support sustainable manufacturing.
The Future of Aluminum Extrusion
The future of aluminum extrusion is moving toward greater design flexibility, smarter production, and broader industrial adoption. For instance, 3D printing is playing an increasingly important role in the design stage by enabling designers to rapidly prototype cross-sectional shapes using plastic models. This allows for early testing of form, fit, and assembly before committing to expensive die fabrication. In industries like aerospace, high-speed rail, and Formula One racing—where lightweight integration and complex geometry are essential—this early-stage validation is especially valuable.
Manufacturing is also evolving, with automation systems improving efficiency, lowering costs, and enabling more customized production. Machines like the JIH-NC24L NC Sawing Machine support this shift by offering high-speed, high-precision cutting of extruded aluminum profiles, helping manufacturers meet growing demands for speed and quality in mass production.
At the same time, the demand for lightweight, sustainable materials continues to grow. Aluminum’s strength, recyclability, and corrosion resistance position it as a key material for industries aiming to meet stricter environmental standards while enhancing performance.
FAQ: Common Questions About Aluminum Extrusion Process
Q1: Is there a minimum wall thickness for aluminum extruded products?
A1: The minimum wall thickness depends on both the design requirements and the production process. In general, aluminum extrusions can achieve wall thicknesses as thin as 0.8 mm, but the exact value should be determined based on the product's intended use and structural needs.
Q2: What surface treatment options are available for aluminum extrusions?
A2: Common surface treatments include anodizing, powder coating, and chemical surface treatments. These methods enhance corrosion resistance, improve appearance, and can extend the service life of aluminum products.
Q3: Is there a length limit for aluminum extruded profiles?
A3: The maximum length of an aluminum extrusion is limited by production equipment and transportation logistics. Typically, extrusion machines can produce profiles up to 6 meters or longer. However, for ease of transportation, installation, and handling, profiles are often cut to custom lengths after extrusion. Production capacities may vary between manufacturers, so it’s important to confirm feasible size ranges with your supplier during the design phase.
Conclusion
As industries continue to demand lightweight, sustainable, and highly customizable solutions, aluminum extrusion stands out as a vital manufacturing technology.
From smarter designs made possible by 3D printing to increasingly automated and efficient production lines, the world of aluminum extrusion is evolving fast — opening new opportunities across construction, transportation, aerospace, and electronics.
If you're looking for expert solutions in aluminum profile machining and precision cutting, contact JIH-I Machinery today. With advanced CNC machining centers and high-performance sawing equipment, JIH-I is ready to support your production needs and help you shape the future.